Embark on an illuminating journey into the Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the mysteries of genetic inheritance. This authoritative resource empowers you with a profound understanding of the fundamental principles governing the transmission of traits and characteristics across generations, shaping the very fabric of human existence.
Through an exploration of Mendelian inheritance, non-Mendelian inheritance, complex traits, genetic variation, and cutting-edge genetic technologies, this answer key provides an indispensable foundation for deciphering the intricacies of human genetics. Prepare to unravel the secrets of heredity and gain invaluable insights into the genetic tapestry that weaves the human experience.
1. Introduction
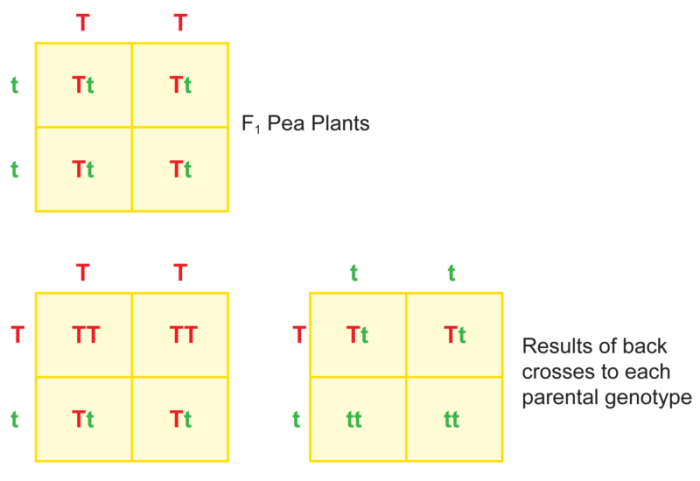
Understanding patterns of heredity is crucial in human genetics, as it helps us unravel the mechanisms behind the inheritance of traits and the development of genetic diseases. Genetics plays a pivotal role in shaping our physical characteristics, personality traits, and susceptibility to various conditions.
2. Mendelian Inheritance
Gregor Mendel’s groundbreaking experiments laid the foundation for our understanding of inheritance. His laws of inheritance describe the transmission of traits from parents to offspring, including the concepts of dominant and recessive alleles, genotypes, and phenotypes.
Single-Gene Traits
| Genotype | Fenotipe |
|---|---|
| AA | Dominan |
| Aa | Dominan |
| aa | Resesif |
3. Non-Mendelian Inheritance
Exceptions to Mendelian inheritance patterns exist, including incomplete dominance, codominance, and multiple alleles. These variations in inheritance can lead to a wider range of phenotypic expressions.
Types of Non-Mendelian Inheritance
| Jenis | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
| Incomplete Dominance | Neither allele is dominant, resulting in an intermediate phenotype. |
| Codominance | Both alleles are expressed fully in the phenotype. |
| Multiple Alleles | More than two alleles exist for a particular gene, leading to multiple phenotypic variations. |
4. Complex Traits
Many human traits are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors, known as polygenic inheritance. These complex traits exhibit continuous variation and are highly susceptible to environmental influences.
Examples of Complex Traits
- Height
- Skin color
- Disease susceptibility
5. Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is the foundation for adaptation and evolution. It arises from mutations, genetic recombination, and gene flow, contributing to the diversity of traits within populations.
Sources of Genetic Variation, Patterns of heredity and human genetics answer key
- Mutations
- Genetic Recombination
- Gene Flow
6. Genetic Technologies: Patterns Of Heredity And Human Genetics Answer Key

Advances in genetic technologies, such as DNA sequencing, PCR, and genetic testing, have revolutionized our ability to study patterns of heredity and diagnose genetic diseases. However, these technologies also raise ethical concerns.
Genetic Technologies and Their Applications
| Teknologi | Aplikasi | Keterbatasan |
|---|---|---|
| DNA Sequencing | Determine the sequence of nucleotides in DNA. | Costly and time-consuming. |
| PCR | Amplify specific DNA sequences. | Can introduce errors. |
| Genetic Testing | Identify genetic mutations associated with diseases. | May not be available for all diseases. |
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of understanding patterns of heredity in human genetics?
Understanding patterns of heredity in human genetics is crucial for comprehending the inheritance of traits and diseases, predicting genetic risks, and developing targeted therapies.
How do genetic technologies contribute to the study of patterns of heredity?
Genetic technologies, such as DNA sequencing and genetic testing, enable researchers to analyze genetic material, identify mutations, and trace inheritance patterns, providing valuable insights into the genetic basis of traits and diseases.