Breaking from convention not conforming to a norm – Breaking from convention and not conforming to societal norms has captivated human history, with individuals and groups challenging established expectations to shape culture, drive innovation, and ignite social change. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of non-conformity, exploring its forms, impacts, motivations, and ethical implications.
From the rebellious artists who defied artistic conventions to the activists who fought for social justice, non-conformists have left an indelible mark on our world. Their stories and experiences offer valuable insights into the power of individuality, the complexities of social norms, and the transformative potential of challenging the status quo.
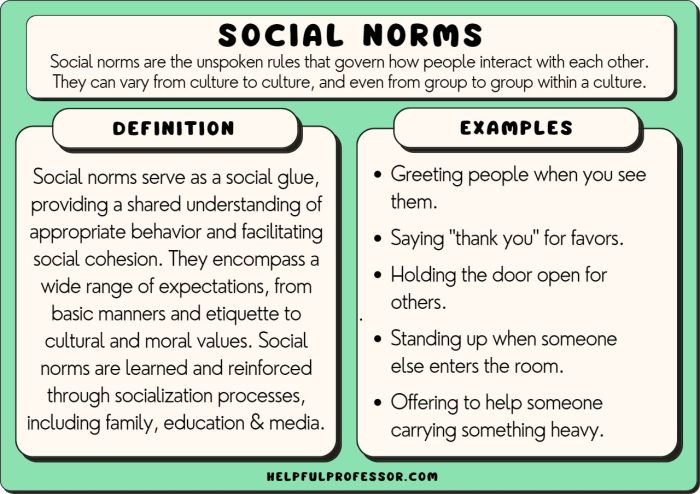
Understanding Non-Conformity

Non-conformity refers to the act of breaking away from established conventions and norms. It involves challenging societal expectations and expressing individuality. Individuals or groups who exhibit non-conformity may face social disapproval or even ostracism, but they also play a crucial role in driving social change and innovation.Examples
of non-conformists include Rosa Parks, who refused to give up her seat on a segregated bus, and Mahatma Gandhi, who led a nonviolent movement for Indian independence. Non-conformity can manifest in various forms, including artistic expression, fashion choices, behavioral patterns, and intellectual pursuits.
Forms of Non-Conformity
Non-conformity can be expressed through diverse channels, each serving as a means of challenging societal expectations.
- Art:Non-conformist artists push creative boundaries, experimenting with unconventional techniques and themes to provoke thought and challenge norms.
- Fashion:Non-conformists often use fashion as a medium of self-expression, breaking away from mainstream trends and embracing unique styles that reflect their individuality.
- Behavior:Non-conformists may engage in unconventional behaviors that deviate from societal norms, such as pursuing alternative lifestyles or challenging social conventions.
- Thought:Non-conformist thinkers question established beliefs and assumptions, challenging conventional wisdom and proposing innovative ideas.
Throughout history, non-conformist movements have emerged, such as the Dadaism art movement in the early 20th century and the counterculture movement of the 1960s. These movements challenged societal norms and paved the way for new artistic and social expressions.
Social and Cultural Impacts of Non-Conformity: Breaking From Convention Not Conforming To A Norm
Non-conformity has significant impacts on social norms and values. It can challenge the status quo, promote diversity, and drive social change.
- Challenging Social Norms:Non-conformists question and disrupt established social norms, forcing society to confront its own assumptions and values.
- Promoting Diversity:Non-conformity fosters diversity by encouraging individuals to embrace their unique identities and express themselves freely.
- Driving Social Change:Non-conformists often play a pivotal role in driving social change by challenging oppressive systems and advocating for marginalized groups.
However, non-conformists may also face challenges and obstacles in society, including social disapproval, discrimination, and even violence.
Individual Perspectives on Non-Conformity

Non-conformists are motivated by a range of factors, including the desire for individuality, a sense of justice, and a belief in the power of change.
- Desire for Individuality:Non-conformists value their uniqueness and strive to express their individuality, even if it means breaking away from societal expectations.
- Sense of Justice:Some non-conformists are driven by a sense of injustice or a desire to challenge oppressive systems.
- Belief in Change:Non-conformists often believe in the power of change and are willing to take risks to challenge the status quo.
The lived experiences of non-conformists vary widely, but they often share a common thread of resilience and determination.
The Role of Non-Conformity in Creative Expression

Non-conformity plays a crucial role in creative expression, fostering innovation and pushing artistic boundaries.
- Fostering Innovation:Non-conformist artists and thinkers challenge conventional ideas and techniques, leading to new and innovative forms of creative expression.
- Pushing Boundaries:Non-conformity encourages artists to push creative boundaries, exploring unconventional themes and experimenting with new forms of expression.
Throughout history, numerous artists, musicians, and writers have embraced non-conformity, breaking away from established norms and creating groundbreaking works that have shaped the course of art and culture.
Ethical Considerations in Non-Conformity
Non-conformity raises ethical considerations, as it may challenge societal values and norms.
- Balancing Individual Expression and Societal Expectations:Non-conformists must navigate the tension between expressing their individuality and respecting societal expectations.
- Potential for Harm:In some cases, non-conformity may have unintended negative consequences, such as causing offense or harm to others.
Ethical guidelines for non-conformity include respecting the rights and values of others, avoiding causing harm, and engaging in constructive dialogue to promote understanding and tolerance.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the potential benefits of non-conformity?
Non-conformity can foster creativity, innovation, and social progress. It challenges established norms, encourages critical thinking, and allows individuals to express their unique perspectives and ideas.
What are some common forms of non-conformity?
Non-conformity can manifest in various ways, including through art, fashion, behavior, and thought. It can involve challenging social conventions, questioning authority, or expressing alternative viewpoints.
What are the ethical considerations related to non-conformity?
Non-conformity raises ethical questions about the balance between individual expression and societal expectations. It is important to navigate these dilemmas with respect for both individual rights and social norms.