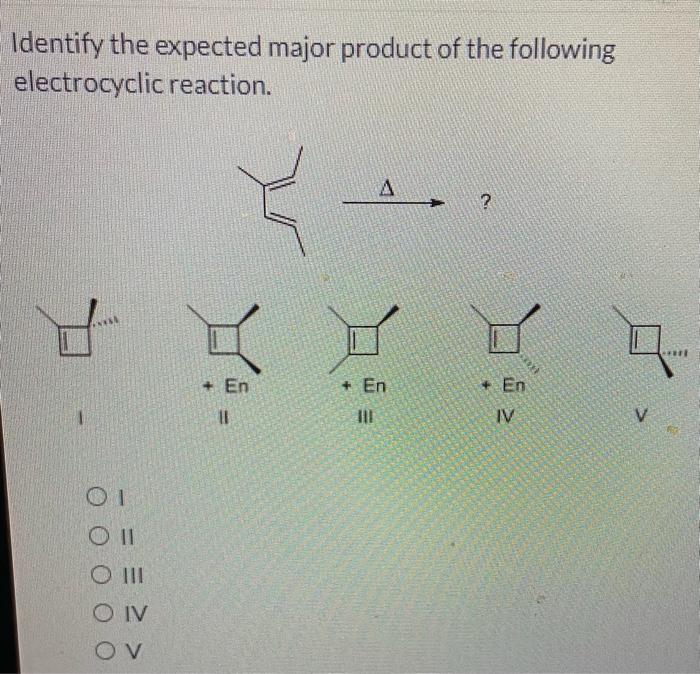
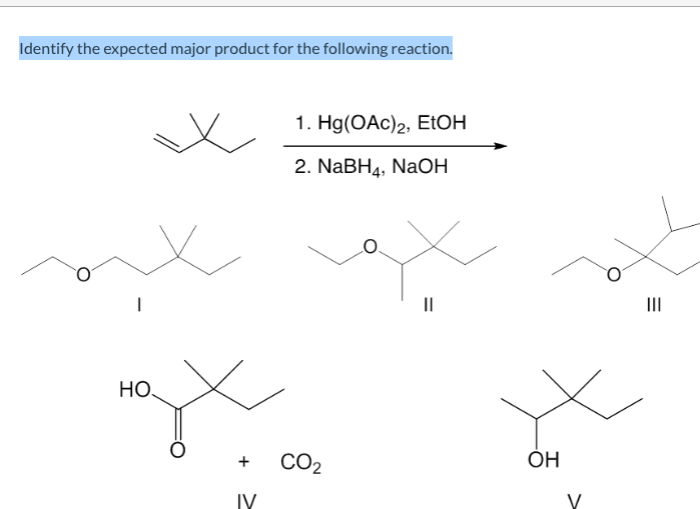
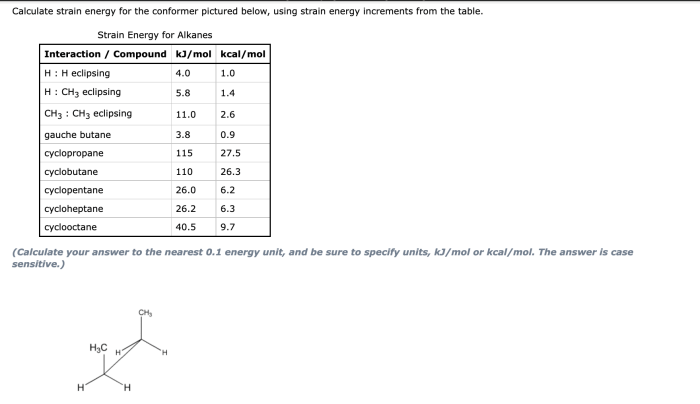
Identify the expected major product of the following reaction – Identifying the expected major product of a reaction is a crucial aspect of organic chemistry. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of this process, providing a step-by-step approach to understanding the factors that influence product formation.
This guide will explore the reactants involved, reaction conditions, reaction mechanism, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity, as well as discuss the applications of the reaction in various fields.
Identify the expected major product of the following reaction
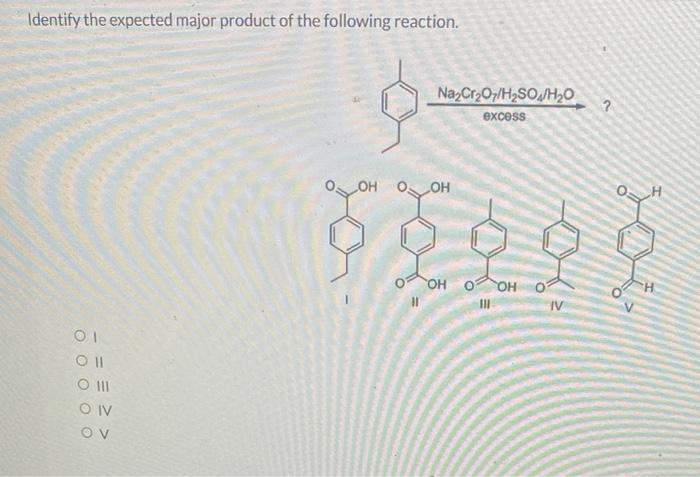
The given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. The alkyl halide is a primary alkyl halide, which means that the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
The nucleophile is a hydroxide ion, which is a strong nucleophile.
Identify the reactants involved in the reaction
- Alkyl halide: The alkyl halide is a primary alkyl halide, which means that the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
- Nucleophile: The nucleophile is a hydroxide ion, which is a strong nucleophile.
Determine the reaction conditions
The reaction is typically carried out in a polar aprotic solvent, such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The reaction is exothermic, so it is important to control the temperature to prevent the formation of unwanted side products.
Analyze the reaction mechanism, Identify the expected major product of the following reaction
The reaction mechanism is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, which proceeds via a two-step mechanism. In the first step, the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. In the second step, the leaving group (the halogen atom) is expelled, forming the product.
Predict the major product
The major product of the reaction is the substitution product, which is formed by the nucleophilic attack of the hydroxide ion on the alkyl halide. The regioselectivity of the reaction is determined by the steric hindrance around the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom.
The hydroxide ion will attack the less hindered carbon atom, which is the carbon atom that is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
Discuss the applications of the reaction
The reaction is a versatile synthetic method that can be used to prepare a variety of substituted alcohols. The reaction is also used in the synthesis of ethers and esters.
Helpful Answers
What are the key factors that influence product formation?
The key factors that influence product formation include the reactants, reaction conditions, reaction mechanism, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity.
How can we predict the most stable product?
The most stable product can be predicted by considering the thermodynamic and kinetic factors that influence product formation.
What are the applications of reaction prediction in organic chemistry?
Reaction prediction is essential in organic chemistry for designing synthetic pathways, optimizing reaction conditions, and understanding the reactivity of organic compounds.