Lesson 20 getting connected ionic compounds – In lesson 20, we delve into the fascinating world of ionic compounds, exploring their unique characteristics, formation, properties, and diverse applications. From their role in everyday life to their cutting-edge uses in advanced technologies, ionic compounds play a crucial part in shaping our understanding of chemistry and its practical implications.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the fundamental concepts of ionic bonding, examining how electron transfer leads to the formation of these compounds. We will delve into their physical and chemical properties, exploring how ionic bond strength influences their behavior.
Moreover, we will investigate the practical applications of ionic compounds, highlighting their significance in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to construction.
Query Resolution: Lesson 20 Getting Connected Ionic Compounds
What are ionic compounds?
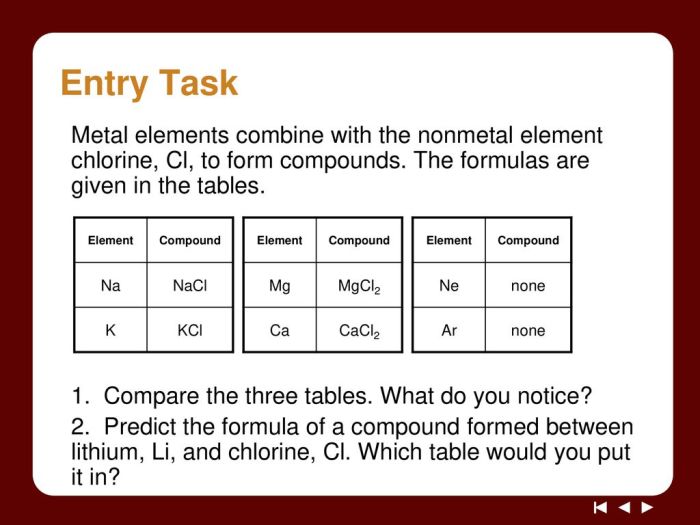
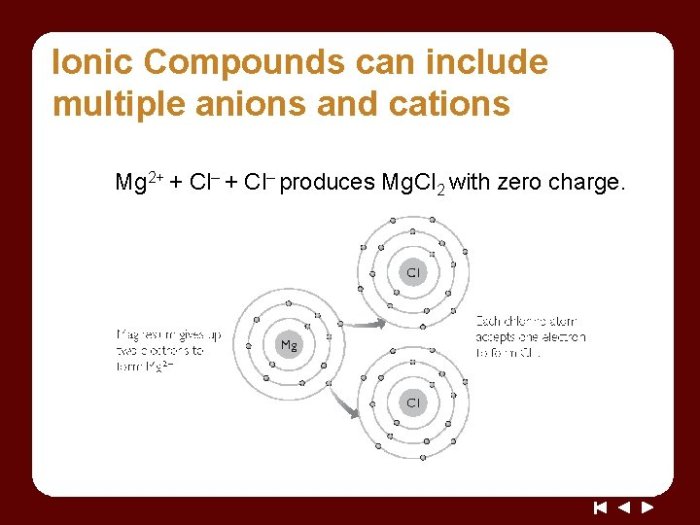
Ionic compounds are formed when a metal loses one or more electrons to a nonmetal, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions).
How do ionic bonds form?
Ionic bonds form when the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions overcomes the repulsive forces between their electron clouds.
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, are soluble in water, and conduct electricity when dissolved or molten.
What are some applications of ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds are used in a wide range of applications, including as electrolytes in batteries, as catalysts in chemical reactions, and as ingredients in fertilizers and building materials.