Embark on a captivating journey through the realm of matter with our interactive Building Blocks of Matter Crossword Puzzle. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of atoms, molecules, and the fundamental particles that shape our universe.
Delve into the intricate structure of matter, explore the properties that govern its behavior, and witness the dynamic interactions that drive chemical reactions. Each solved clue brings you closer to understanding the very essence of the physical world.
Definition of Building Blocks of Matter
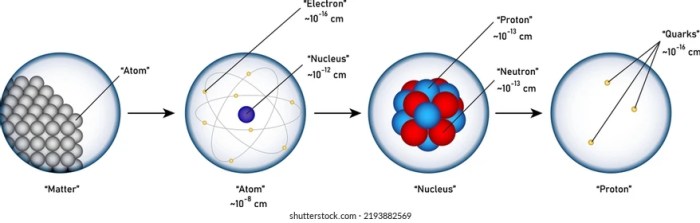
The building blocks of matter refer to the fundamental units that constitute all matter in the universe. These basic units are subatomic particles, which include protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
Subatomic Particles
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of an atom and determine its atomic number.
- Neutrons: Uncharged particles found in the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of an atom but do not affect its atomic number.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. They are responsible for the chemical properties of an atom.
Atoms and Molecules
Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain the properties of an element. They consist of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Molecules are formed when atoms combine chemically.
Structure of Building Blocks of Matter
Atomic Structure
Atoms are composed of a central nucleus surrounded by electron shells. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electron shells contain electrons.
Atomic Number and Mass Number, Building blocks of matter crossword
The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus. It determines the element to which the atom belongs. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Electron Shells
Electrons occupy specific energy levels called electron shells. The first shell can hold up to 2 electrons, the second shell can hold up to 8 electrons, and so on.
Properties of Building Blocks of Matter
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of an element are determined by the number and arrangement of electrons in its electron shells. Elements with similar electron configurations exhibit similar chemical properties.
Periodic Table
The periodic table organizes elements according to their atomic number and electron configuration. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of matter, such as density and melting point, are influenced by the arrangement of its building blocks. For example, denser materials have more closely packed atoms.
Building Blocks of Matter in Chemical Reactions
Chemical Bonds
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of building blocks of matter. Atoms can form chemical bonds with each other to create molecules. There are different types of chemical bonds, including covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
Role in Chemical Reactions
The building blocks of matter determine the chemical reactions that an element or molecule can undergo. For example, atoms with unpaired electrons are more likely to react with other atoms to form bonds.
Applications of Understanding Building Blocks of Matter
Material Science and Nanotechnology
Understanding the building blocks of matter has led to advancements in material science and nanotechnology. By manipulating the arrangement of atoms, scientists can create materials with specific properties.
Medicine and Biotechnology
Knowledge of building blocks of matter has also contributed to advancements in medicine and biotechnology. For example, understanding the structure of proteins has led to the development of new drugs.
Question & Answer Hub: Building Blocks Of Matter Crossword
What are the fundamental particles that make up matter?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the subatomic particles that constitute matter.
What is the role of the nucleus in an atom?
The nucleus, located at the center of an atom, contains protons and neutrons and is responsible for the atom’s mass and positive charge.
How do chemical bonds form?
Chemical bonds are formed when atoms share or transfer electrons, resulting in the formation of molecules or compounds.
