Aphg unit 7 practice test – Prepare for success in your AP Human Geography exam with our comprehensive practice test for Unit 7. This engaging and informative test covers all the crucial topics you need to master for the exam.
Our practice test is designed to provide you with a realistic simulation of the actual exam experience. By taking this test, you can assess your knowledge, identify areas for improvement, and build confidence in your ability to perform well on the real thing.
Introduction
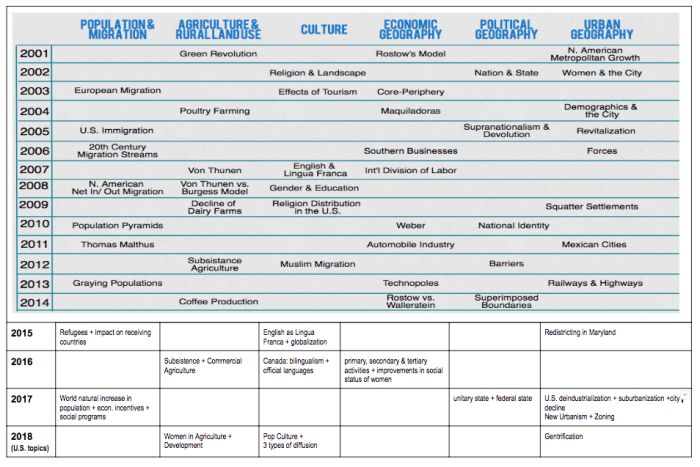
This practice test is designed to help you assess your understanding of the concepts covered in Unit 7 of AP Human Geography. Unit 7 focuses on the patterns and processes of cultural geography, including language, religion, ethnicity, and migration.
Language
- Language is a system of communication used by a community or group of people.
- Languages can be classified into different families based on their linguistic similarities.
- The distribution of languages around the world is influenced by factors such as history, migration, and trade.
Religion
- Religion is a system of beliefs and practices that relate humanity to spirituality and moral values.
- Religions can be classified into different types, such as monotheistic, polytheistic, and animistic.
- The distribution of religions around the world is influenced by factors such as history, culture, and politics.
Ethnicity, Aphg unit 7 practice test
- Ethnicity is a sense of belonging to a group of people who share a common culture, history, and language.
- Ethnic groups can be found in all parts of the world, and their identities can be based on a variety of factors, such as race, religion, or language.
Migration
- Migration is the movement of people from one place to another.
- Migrants can be classified into different types, such as refugees, economic migrants, and environmental migrants.
- The movement of people around the world is influenced by factors such as war, poverty, and environmental disasters.
Section 1: Human Population: Aphg Unit 7 Practice Test

Population dynamics are influenced by a complex interplay of factors that determine its growth or decline. Understanding these factors is crucial for addressing population-related challenges and ensuring sustainable development.
Factors Affecting Population Growth and Decline
Factors affecting population change include:
- Fertility Rates:The average number of children born per woman influences population growth. High fertility rates can lead to rapid population increase, while low rates can result in population decline.
- Mortality Rates:The number of deaths per 1,000 people affects population size. High mortality rates, often caused by diseases, malnutrition, or conflict, can reduce population growth or even lead to decline.
- Migration:The movement of people into or out of a region can significantly impact population size. Immigration can boost population growth, while emigration can lead to decline.
- Age Structure:The proportion of different age groups in a population influences its growth potential. A high proportion of young people can lead to rapid population growth, while a large elderly population can slow growth or even cause decline.
Carrying Capacity
The concept of carrying capacity refers to the maximum population size that an environment can sustain without degrading its resources or compromising its ability to support life. Exceeding carrying capacity can lead to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and a decline in living standards.
Section 2: Migration
Migration is the movement of people from one place to another, either across borders or within a country. It can be temporary or permanent, and it can be voluntary or forced. Migration has been a part of human history for centuries, and it continues to shape the world today.
There are many different types of migration, each with its own unique causes and consequences. Some of the most common types of migration include:
- Economic migration:This is the movement of people from one place to another in search of better economic opportunities. This can include both skilled and unskilled workers, and it can be temporary or permanent.
- Political migration:This is the movement of people from one place to another due to political persecution or conflict. This can include refugees, asylum seekers, and internally displaced persons.
- Environmental migration:This is the movement of people from one place to another due to environmental factors, such as climate change, natural disasters, or pollution.
- Social migration:This is the movement of people from one place to another due to social factors, such as family reunification, marriage, or education.
The factors that motivate people to migrate are complex and varied. Some of the most common factors include:
- Economic factors:These include factors such as poverty, unemployment, and lack of economic opportunity.
- Political factors:These include factors such as war, persecution, and political instability.
- Environmental factors:These include factors such as climate change, natural disasters, and pollution.
- Social factors:These include factors such as family reunification, marriage, and education.
Migration can have a significant impact on both sending and receiving countries. In sending countries, migration can lead to a loss of skilled workers, a decline in population, and a decrease in economic activity. In receiving countries, migration can lead to an increase in population, a more diverse population, and a boost to the economy.
Brain Drain
Brain drain is the emigration of highly skilled workers from a developing country to a developed country. This can have a negative impact on the developing country, as it can lead to a loss of skilled workers and a decline in economic growth.
Cracking the APHG Unit 7 Practice Test requires a solid understanding of various musical concepts. One such concept is the G minor scale in bass clef. Understanding how to play this scale can help you ace the test. Refer to g minor scale bass clef for a detailed guide and practice exercises.
This knowledge will enhance your overall performance on the APHG Unit 7 Practice Test.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to brain drain, including:
- Economic factors:These include factors such as higher salaries, better working conditions, and more opportunities for advancement in developed countries.
- Political factors:These include factors such as political instability, corruption, and a lack of freedom in developing countries.
- Social factors:These include factors such as a lack of educational opportunities, a lack of healthcare, and a lack of safety in developing countries.
Brain drain can have a number of negative consequences for developing countries. These include:
- A loss of skilled workers
- A decline in economic growth
- A decrease in innovation
- A decline in the quality of life
There are a number of things that can be done to address brain drain. These include:
- Improving economic conditions in developing countries
- Promoting political stability and democracy in developing countries
- Investing in education and healthcare in developing countries
- Creating more opportunities for skilled workers in developing countries
Section 3: Urbanization
Urbanization refers to the increasing concentration of people in urban areas, such as cities and towns. This phenomenon has been driven by various factors, including:
- Economic opportunities:Cities offer better job prospects, higher wages, and access to markets.
- Technological advancements:Transportation and communication technologies have made it easier for people to move to and live in urban areas.
- Political and social changes:Industrialization, globalization, and urbanization have led to a shift in the balance of power and resources toward cities.
- Environmental factors:Rural areas may face challenges such as droughts, floods, or soil degradation, driving people to urban areas.
Social, Economic, and Environmental Challenges of Urbanization
While urbanization brings benefits, it also poses challenges:
- Social:Overcrowding, poverty, crime, and social inequality can be prevalent in urban areas.
- Economic:Urbanization can lead to income disparities, housing shortages, and infrastructure strain.
- Environmental:Cities contribute to air pollution, water scarcity, waste generation, and urban heat island effects.
Sustainable Urbanization
Sustainable urbanization aims to address these challenges while promoting the well-being of urban residents and the environment. Strategies include:
- Compact and mixed-use development:Creating dense, walkable neighborhoods with a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational areas.
- Efficient transportation:Promoting public transportation, cycling, and walking to reduce traffic congestion and pollution.
- Green infrastructure:Incorporating parks, green roofs, and rainwater harvesting systems to mitigate environmental impacts.
- Community engagement:Involving residents in decision-making and urban planning to ensure their needs are met.
- Economic diversification:Promoting a diverse range of industries to reduce reliance on a single economic sector.
Section 4: Health and Disease

Health and disease are fundamental aspects of human existence, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. This section delves into the various elements that shape human health, including environmental, social, and economic conditions. It also explores the different types of diseases and their transmission modes, highlighting the challenges of addressing health issues in developing countries.
Environmental Factors
- Air Pollution:Exposure to pollutants such as particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer.
- Water Contamination:Contaminated water sources can transmit waterborne diseases like diarrhea, typhoid, and cholera.
- Climate Change:Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can lead to heat-related illnesses, respiratory issues, and infectious diseases.
Social Factors
- Access to Healthcare:Availability and affordability of healthcare services significantly impact health outcomes.
- Education and Health Literacy:Knowledge about health risks and preventive measures promotes healthy behaviors.
- Social Support:Strong social connections and support networks contribute to mental and physical well-being.
Economic Factors
- Income and Poverty:Low income and poverty often limit access to nutritious food, clean water, and adequate housing, leading to health disparities.
- Employment Conditions:Hazardous work environments and long working hours can contribute to physical and mental health problems.
- Economic Development:Economic growth can improve health outcomes by providing better sanitation, nutrition, and healthcare infrastructure.
Types of Diseases
Diseases can be classified into various categories based on their transmission mode and causative agents:
- Communicable Diseases:Spread through contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated object (e.g., influenza, measles, HIV/AIDS).
- Non-Communicable Diseases:Chronic conditions that develop over time due to genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, cancer).
- Zoonotic Diseases:Transmitted from animals to humans (e.g., rabies, Lyme disease, avian influenza).
Global Health
Global health focuses on addressing health issues that transcend national borders, such as infectious disease outbreaks, environmental pollution, and chronic disease management. Challenges in developing countries include:
- Limited Healthcare Infrastructure:Lack of hospitals, clinics, and medical equipment.
- Shortage of Healthcare Professionals:Insufficient number of doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers.
- Cultural Barriers:Misconceptions and stigma surrounding certain diseases can hinder prevention and treatment efforts.
Question Bank
What topics are covered in the APHG Unit 7 practice test?
The practice test covers all the essential topics from APHG Unit 7, including human population, migration, urbanization, and health and disease.
How long should I spend on the practice test?
The practice test is designed to be completed in approximately 60 minutes, which is the same time limit as the actual exam.
What should I do after completing the practice test?
Once you have completed the practice test, review your answers and identify any areas where you need to improve. Focus your studies on these areas to enhance your overall understanding and exam readiness.